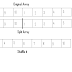
In computer science, a queue (/ˈkjuː/ kew) is a particular kind of abstract data type or collection in which the entities in the collection are kept in order and the principal (or only) operations on the collection are the addition of entities to the rear terminal position, known as enqueue, and removal of entities from the front terminal position, known as dequeue. This makes the queue a First-In-First-Out (FIFO) data structure. In a FIFO data structure, the first element added to the queue will be the first one to be removed. This is equivalent to the requirement that once a new element is added, all elements that were added before have to be removed before the new element can be removed. Often a peek or front operation is also entered, returning the value of the front element without dequeuing it. A queue is an example of a linear data structure, or more abstractly a sequential collection. Queues provide services in computer science, transport, and operations research where various entities such as data, objects, persons, or events are stored and held to be processed later. In these contexts, the queue performs the function of a buffer. Queues are common in computer programs, where they are implemented as data structures coupled with access routines, as an abstract data structure or in object-oriented languages as classes. Common implementations are circular buffers and linked lists. More information can be achieved by clicking this link.
Queue Class
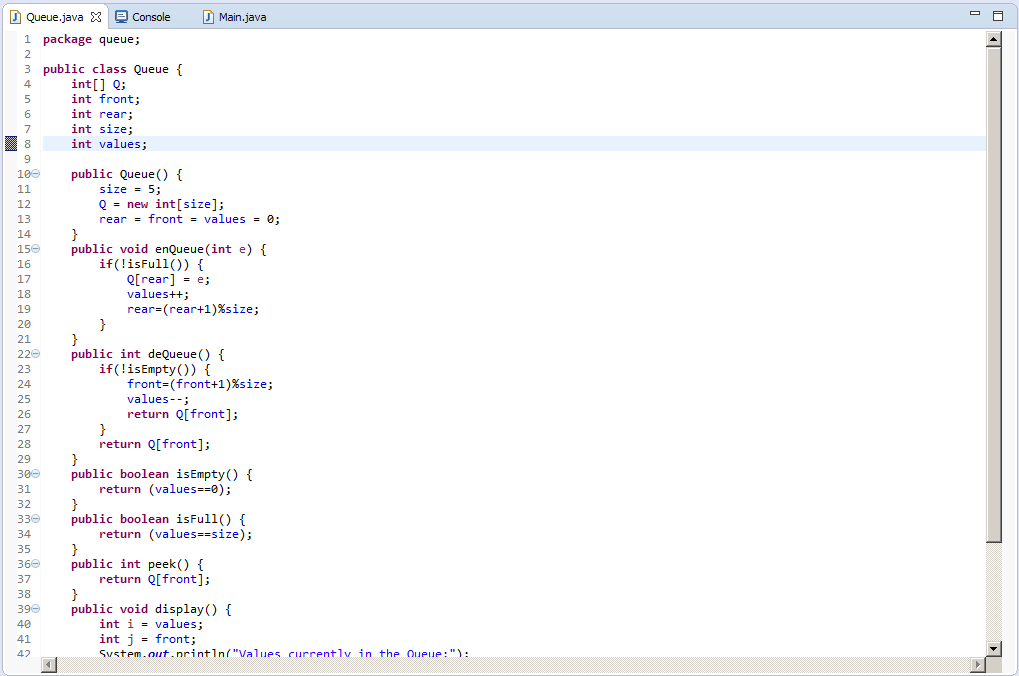
package queue;
public class Queue {
int[] Q;
int front;
int rear;
int size;
int values;
public Queue() {
size = 5;
Q = new int[size];
rear = front = values = 0;
}
public void enQueue(int e) {
if(!isFull()) {
Q[rear] = e;
values++;
rear=(rear+1)%size;
}
}
public int deQueue() {
front=(front+1)%size;
values--;
return Q[front-1];
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return (values==0);
}
public boolean isFull() {
return (values==size);
}
public int peek() {
return Q[front];
}
public void display() {
int i = values;
int j = front;
System.out.println("Values currently in the Queue:");
while(i>0) {
i--;
System.out.println(Q[j]);
j=(j+1)%size;
}
}
}
Main class
package queue;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue q = new Queue();
q.enQueue(1);
q.enQueue(1);
q.enQueue(1);
q.enQueue(1);
q.deQueue();
q.deQueue();
q.deQueue();
q.enQueue(2);
q.enQueue(3);
q.enQueue(4);
q.enQueue(5);
q.display();
}
}
There's no big difference between the code in Java/C++ it's just the syntax you get used to ;). C++ version of integer Queue.
Click the download zip button to download the complete package exported by Eclipse IDE.


.png)



No comments :
Post a Comment